
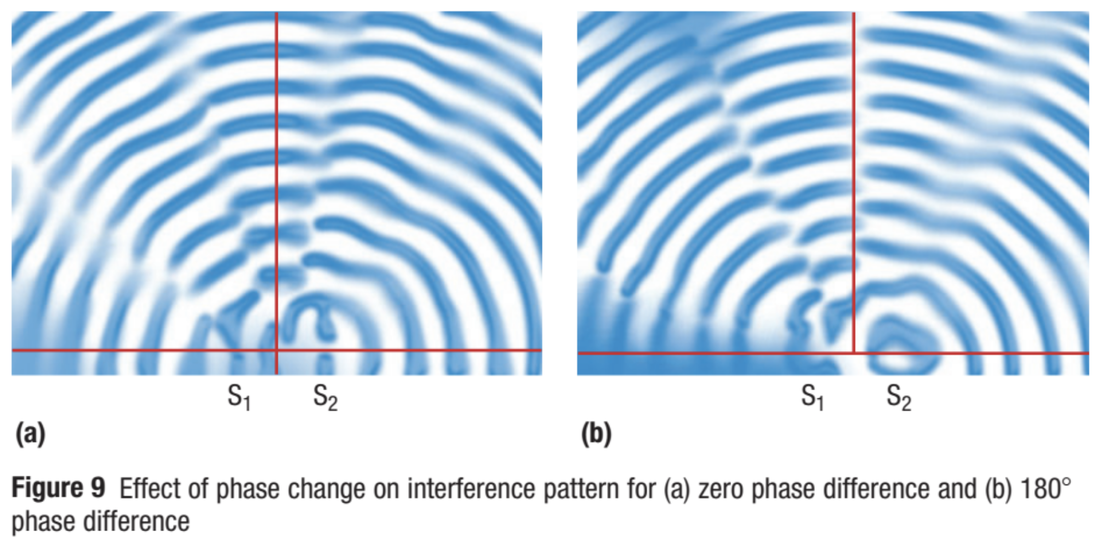
The spatial arrangement of the fringes depends on the slit we have chosen for the diffraction experiment. Are the fringes obtained from diffraction equally spaced? If a monochromatic light wave is passed through a double slit, first they get diffracted at the corner of the slit, and then the two diffracted light waves superimpose on one another, causing the interference. Interference refers to the superposition of two or more coherent light waves. Yes, in some cases, the diffraction can cause interference.
The width of the slit should be sufficiently narrow to get good diffraction fringes. The wavelength of the light should match the width of the aperture used. (The diffraction can be achieved using white light, but we get the dispersion of colors as a diffraction pattern). The light has to be monochromatic to achieve a perfect diffraction pattern. The light undergoes diffraction if it possesses the conditions that are listed below. Frequently Asked Questions What are the essential conditions needed for the diffraction of light? The equation we have obtained says that the diffraction is more if a wave of low frequency is incident on the aperture. This gives the relation between the diffraction and frequency as they are inversely related. This gives the diffraction of the wave with a certain frequency of the incident wave. If the angle θ is very small then, sinθ~θ, then the equation will be Where 1.22 is the constant d is the diameter of the aperture and θ is the angle between the incident and diffracted wave. If we have considered the aperture as a circular aperture, the equation can be modified as Replacing the λ in the above equation we get Rearranging the terms, we get frequency as The wavelength can be given in terms of frequency as Where θ is the angle between the incident and diffracted wave. 
The amount of diffraction can be given by the equation, Image to describe the relation between frequency and diffraction Let us suppose that a light wave of wavelength λ is passed through a slit of width d and the light wave s travels in a straight line to give the diffraction fringes. This dependency can be expressed by providing the relation between the frequency and diffraction as given below. Though the frequency of the wave and diffracted wave remains the same before and after the diffraction occurs, diffraction always depends on the frequency. The edge of the object is used as the focal point and generates the new wave front whose frequency will remain the same, but the intensity is reduced.
When a wave of frequency equal to the barrier dimension strikes, they create the mid-frequency range, and the waves are diffracted around the object. The low-frequency sound strikes the obstacle the wavelength of the incident wave is much longer than the barrier thus, the wave can easily pass over the corner of the barrier, creating the wave’s diffraction. When a high-frequency sound wave with a shorter wavelength strikes the obstacle, the waves do not diffract instead, they reflect back around the obstacle, creating the shadow of sound behind the obstacle. If we consider the example of the sound wave, the following facts can be observed: Thus, the incident wave with low frequency must be incident to achieve greater diffraction. Since high frequency refers to shorter wavelength, in the phenomena of diffraction, always wave with greater wavelength diffract more rapidly than the short wavelength. The wave with high frequency diffracts less than the wave with low frequency. Diagram illustrating How does frequency affect diffraction However, the amount of diffraction depends on the frequency of the incident wave. Diffraction pattern of wave illustrating how does frequency affect diffraction Image credits: Image by PublicDomainPictures from Pixabayįrequency is an invariable entity after the diffraction, i.e., the frequency of the incident wave does not change when the wave gets diffracted. 
However, we have learnt the influence of wavelength on diffraction it is so obvious that frequency can also affect the diffraction. How does frequency affect diffraction?Įvery wave propagating in a medium has a certain frequency that is inversely associated with the wavelength. Since diffraction occurs due to the wave striking the corner of the obstacle, does frequency affect diffraction as the wave has a certain frequency? If yes, then let’s learn the relation between frequency and diffraction and how does frequency affect diffraction in detail. In this post, let us learn about the factors affecting diffraction.įrequency refers to the number of waves passing towards a fixed point in a unit of time.

In previous articles, we have studied in brief about diffraction and behavior of light and sound waves to cause diffraction.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
